Buildots, a Tel Aviv and London-based startup that is using computer vision to modernize the construction management industry, today announced that it has raised $16 million in total funding. This includes a $3 million seed round that was previously unreported and a $13 million Series A round, both led by TLV Partners. Other investors include Innogy Ventures, Tidhar Construction Group, Ziv Aviram (co-founder of Mobileye & OrCam), Magma Ventures head Zvika Limon, serial entrepreneurs Benny Schnaider and Avigdor Willenz, as well as Tidhar chairman Gil Geva.
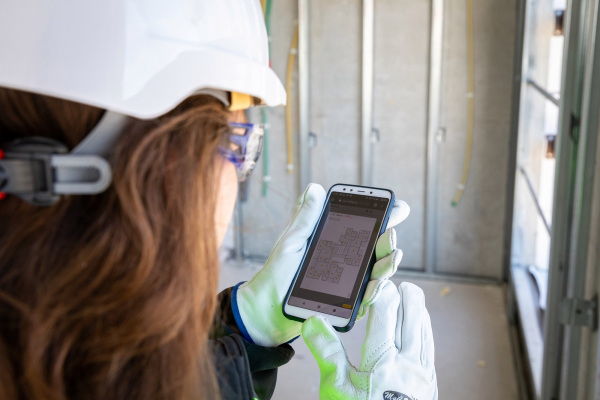
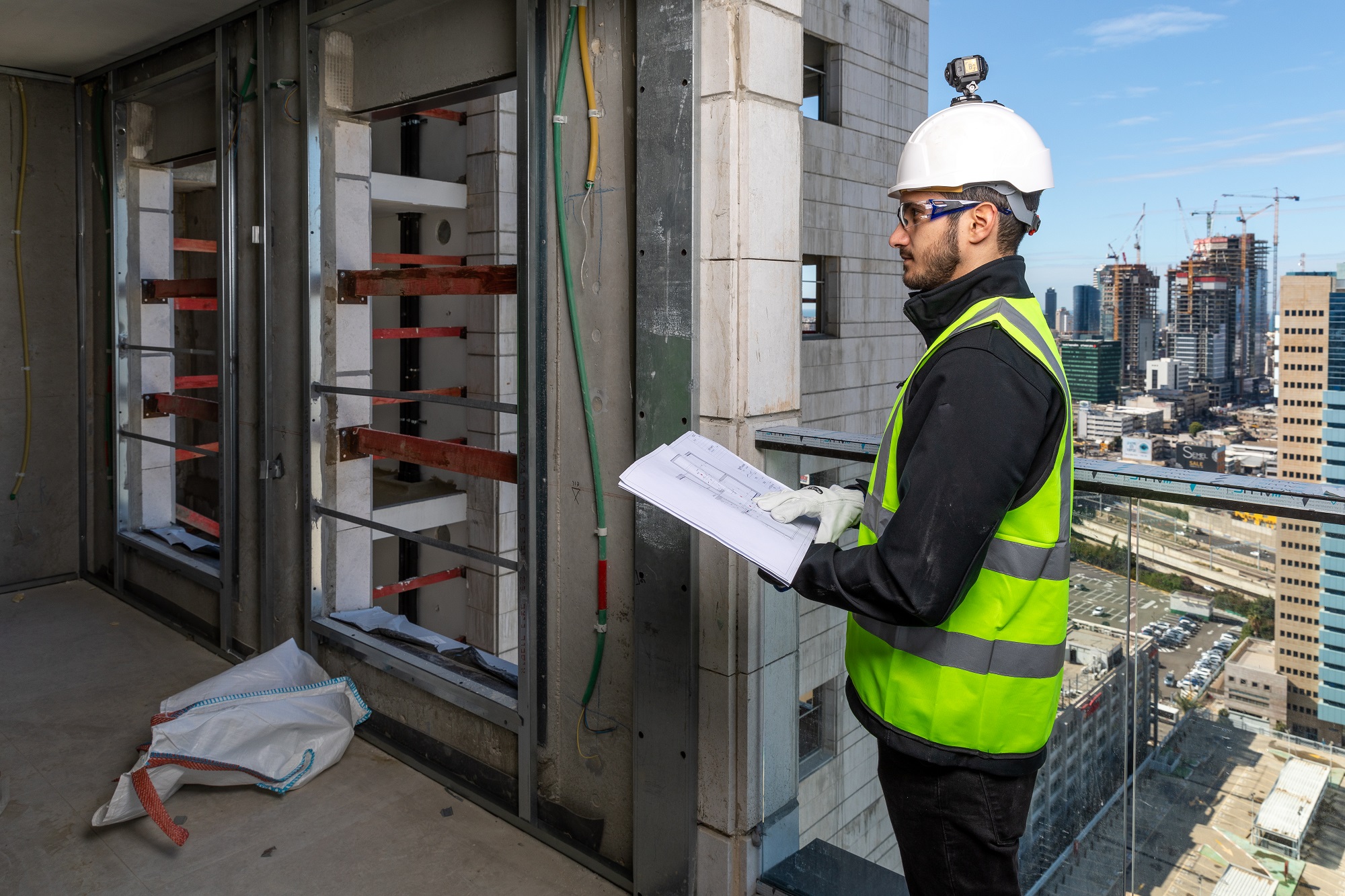
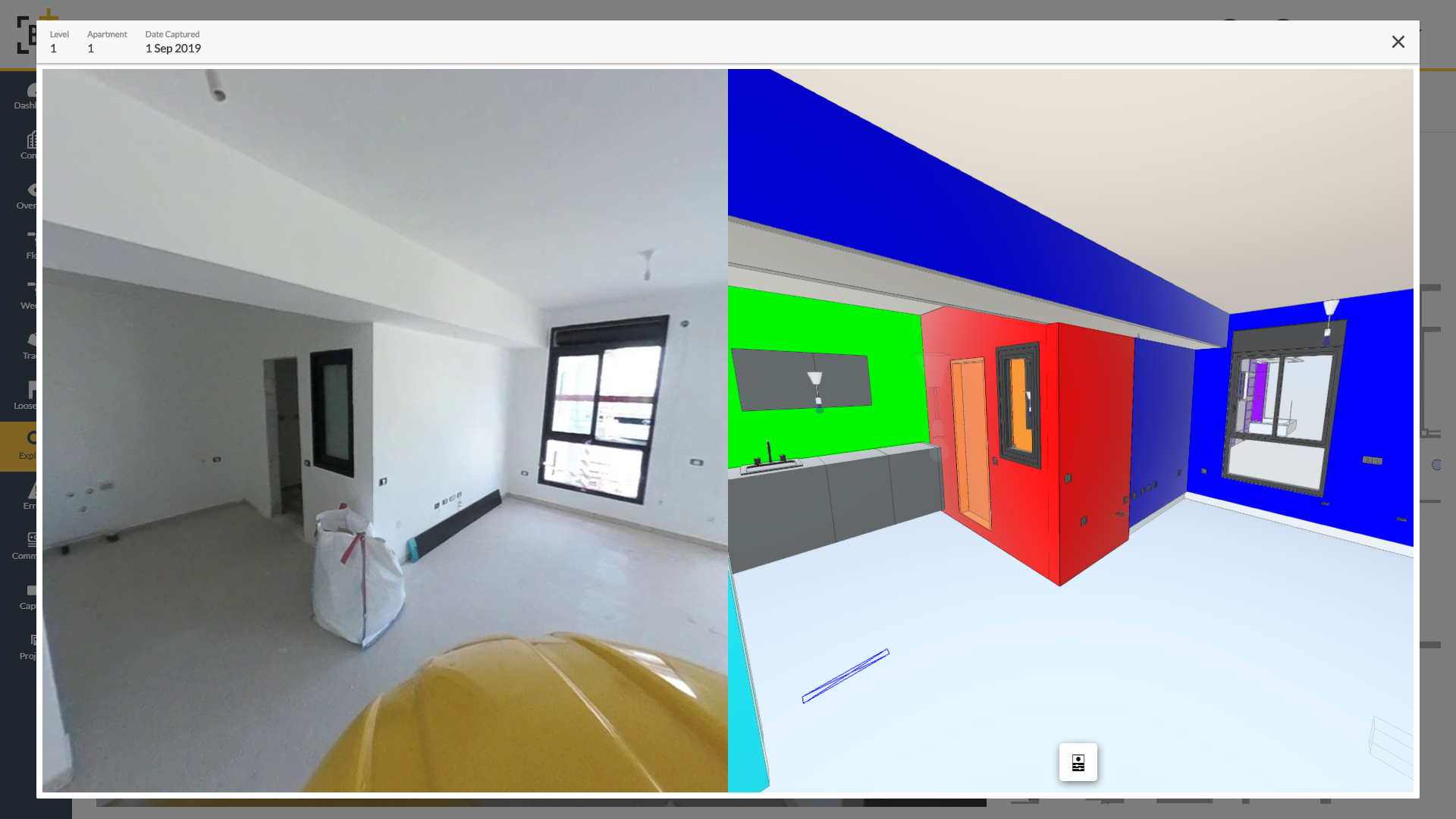
The idea behind Buildots is pretty straightforward. The team is using hardhat-mounted 360-degree cameras to allow project managers at construction sites to get an overview of the state of a project and whether it remains on schedule. The company’s software creates a digital twin of the construction site, using the architectural plans and schedule as its basis, and then uses computer vision to compare what the plans say to the reality that its tools are seeing. With this, Buildots can immediately detect when there’s a power outlet missing in a room or whether there’s a sink that still needs to be installed in a kitchen, for example.
“Buildots have been able to solve a challenge that for many seemed unconquerable, delivering huge potential for changing the way we complete our projects,” said Tidhar’s Geva in a statement. “The combination of an ambitious vision, great team and strong execution abilities quickly led us from being a customer to joining as an investor to take part in their journey.”
The company was co-founded in 2018 by Roy Danon, Aviv Leibovici and Yakir Sundry. Like so many Israeli startups, the founders met during their time in the Israeli Defense Forces, where they graduated from the Talpiot unit.
“At some point, like many of our friends, we had the urge to do something together — to build a company, to start something from scratch,” said Danon, the company’s CEO. “For us, we like getting our hands dirty. We saw most of our friends going into the most standard industries like cloud and cyber and storage and things that obviously people like us feel more comfortable in, but for some reason we had like a bug that said, ‘we want to do something that is a bit harder, that has a bigger impact on the world.’ ”
So the team started looking into how it could bring technology to traditional industries like agriculture, finance and medicine, but then settled upon construction thanks to a chance meeting with a construction company. For the first six months, the team mostly did research in both Israel and London to understand where it could provide value.
Danon argues that the construction industry is essentially a manufacturing industry, but with very outdated control and process management systems that still often relies on Excel to track progress.
Construction sites obviously pose their own problems. There’s often no Wi-Fi, for example, so contractors generally still have to upload their videos manually to Buildots’ servers. They are also three dimensional, so the team had to develop systems to understand on what floor a video was taken, for example, and for large indoor spaces, GPS won’t work either.
The teams tells me that before the COVID-19 lockdowns, it was mostly focused on Israel and the U.K., but the pandemic actually accelerated its push into other geographies. It just started work on a large project in Poland and is scheduled to work on another one in Japan next month.
Because the construction industry is very project-driven, sales often start with getting one project manager on board. That project manager also usually owns the budget for the project, so they can often also sign the check, Danon noted. And once that works out, then the general contractor often wants to talk to the company about a larger enterprise deal.
As for the funding, the company’s Series A round came together just before the lockdowns started. The company managed to bring together an interesting mix of investors from both the construction and technology industries.
Now, the plan is to scale the company, which currently has 35 employees, and figure out even more ways to use the data the service collects and make it useful for its users. “We have a long journey to turn all the data we have into supporting all the workflows on a construction site,” said Danon. “There are so many more things to do and so many more roles to support.”
[ad_2]
Source link